Drugs.com provides accurate and independent information on more than 24,000 prescription drugs, over-the-counter medicines and natural products. This material is provided for educational purposes only and is not intended for medical advice, diagnosis or treatment. Data sources include IBM Watson Micromedex (updated 7 Dec 2020), Cerner Multum™ (updated 4 Dec 2020), ASHP (updated 3 Dec 2020. Or chemicals are defined as drugs with no currently accepted medical use and a high potential for. This is the list of Schedule III drugs as defined by the United States Controlled Substances Act at and 21 CFR 1308.13, with modifications through August 22, 2014 (79 FR 49961).The following findings are required for drugs to be placed in this schedule: The drug or other substance has a potential for abuse less than the drugs or other substances in schedules I and II.
A drug class is a set of medications and other compounds that have similar chemical structures, the same mechanism of action (i.e. binding to the same biological target), a related mode of action, and/or are used to treat the same disease.[1][2]
In several dominant drug classification systems, these four types of classifications form a hierarchy. For example, the fibrates are a chemical class of drugs (amphipathic carboxylic acids) that share the same mechanism of action (PPAR agonist) and mode of action (reducing blood triglycerides), and that are used to prevent and treat the same disease (atherosclerosis). Conversely, not all PPAR agonists are fibrates, not all triglyceride lowering agents are PPAR agonists, and not all drugs used to treat atherosclerosis are triglyceride-lowering agents.
A drug class is typically defined by a prototype drug, the most important, and typically the first developed drug within the class, used as a reference for comparison.

Comprehensive systems[edit]
- Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical Classification System (ATC) - most widely used. Combines classification by organ system and therapeutic, pharmacological, and chemical properties.
- Systematized Nomenclature of Medicine (SNOMED) - includes a section devoted to drug classification
Chemical class[edit]
This type of categorisation of drugs is from a chemical perspective and categorises them by their chemical structure. Examples of drug classes that are based on chemical structures include:
Mechanism of action[edit]
This type of categorisation is from a pharmacological perspective and categorises them by their biological target. Drug classes that share a common molecular mechanism of action by modulating the activity of a specific biological target.[3] The definition of a mechanism of action also includes the type of activity at that biological target. For receptors, these activities include agonist, antagonist, inverse agonist, or modulator. Enzyme target mechanisms include activator or inhibitor. Ion channel modulators include opener or blocker. The following are specific examples of drug classes whose definition is based on a specific mechanism of action:
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug − cyclooxygenase inhibitor
- Statin – HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor
Mode of action[edit]
This type of categorisation of drugs is from a biological perspective and categorises them by the anatomical or functional change they induce. Drug classes that are defined by common modes of action (i.e. the functional or anatomical change they induce) include:
- Diuretic or Antidiuretic
- Inotrope (positive or negative)
- Chronotrope (positive or negative)
Therapeutic class[edit]
Class 1 2 3 Fda
This type of categorisation of drugs is from a medical perspective and categorises them by the pathology they are used to treat. Drug classes that are defined by their therapeutic use (the pathology they are intended to treat) include:
Amalgamated classes[edit]
Some drug classes have been amalgamated from these three principles to meet practical needs. The class of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) is one such example. Strictly speaking, and also historically, the wider class of anti-inflammatory drugs also comprises steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. These drugs were in fact the predominant anti-inflammatories during the decade leading up to the introduction of the term 'nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs'. Because of the disastrous reputation that the corticosteroids had got in the 1950s, the new term, which offered to signal that an anti-inflammatory drug was not a steroid, rapidly gained currency.[4] The drug class of 'nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs' (NSAIDs) is thus composed by one element ('anti-inflammatory') that designates the mechanism of action, and one element ('nonsteroidal') that separates it from other drugs with that same mechanism of action. Similarly, one might argue that the class of disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs (DMARD) is composed by one element ('disease-modifying') that albeit vaguely designates a mechanism of action, and one element ('anti-rheumatic drug') that indicates its therapeutic use.
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID)
- Disease-modifying antirheumatic drug (DMARD)[5]
Other systems of classification[edit]
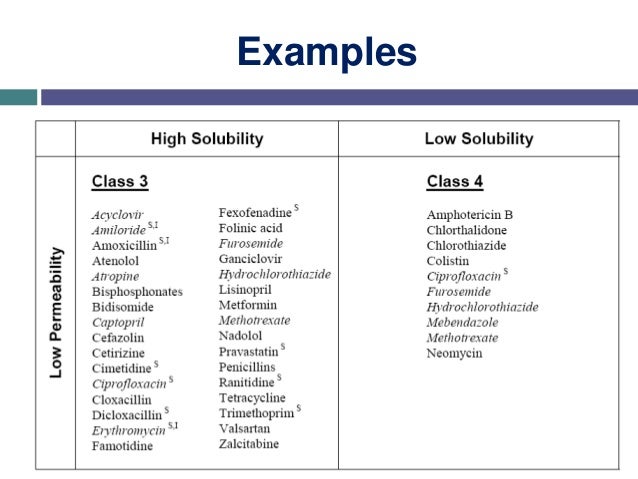
Other systems of drug classification exist, for example the Biopharmaceutics Classification System which determines a drugs' attributes by solubility and intestinal permeability.
Legal classification[edit]
- For the UK legal classification, see Drugs controlled by the UK Misuse of Drugs Act
- For the US legal classification, see Controlled Substances Act § Schedules of controlled substances
- Pregnancy category is defined using a variety of systems by different jurisdictions
Class 1 2 3 Standpipe Systems
References[edit]
- ^Mahoney A, Evans J (2008). 'Comparing drug classification systems'. AMIA Annual Symposium Proceedings: 1039. PMID18999016.
- ^World Health Organization (2003). Introduction to drug utilization research(PDF). Geneva: World Health Organization. p. 33. ISBN978-9241562348.
- ^Imming P, Sinning C, Meyer A (Oct 2006). 'Drugs, their targets and the nature and number of drug targets'. Nature Reviews. Drug Discovery. 5 (10): 821–34. doi:10.1038/nrd2132. PMID17016423.
- ^Buer JK (Oct 2014). 'Origins and impact of the term 'NSAID''. Inflammopharmacology. 22 (5): 263–7. doi:10.1007/s10787-014-0211-2. hdl:10852/45403. PMID25064056.
- ^Buer JK (Aug 2015). 'A history of the term 'DMARD''. Inflammopharmacology. 23 (4): 163–71. doi:10.1007/s10787-015-0232-5. PMC4508364. PMID26002695.
External links[edit]
- 'Drug names and classes'. PubMed Health. United States National Library of Medicine. Retrieved 2015-11-07.
- 'Information by Drug Class'. Drug Safety and Availability. United States Food and Drug Administration. Retrieved 2015-11-07.